JAVA_技巧_如何利用Scanner類別進行輸入(爪哇點矮喔點心)_字元_字串_數字輸入
首先在本篇文章撰寫前中
大家以前是否還習慣著 C 或 C++
以前如果們要實行無限輸入一個整數這種功能的話
我們會怎麼做???
感覺 while 迴圈不可少
首先我們先不要急著 無限輸入
先輸入一個數字 即可
輸入是致命關鍵 不可不會!!!!!
【字元的輸入】
Step1. 請載入 java.io.* 套件 ( 口訣: 爪哇點矮喔點心 / 怕你少輸入 任何一個符號)
Step2. 在 main方法後頭 加上 throws IOException 要加喔!!!!!!
Step3.宣告字元 我們要輸入一個字元型態的鍵盤key-in的任意字符
並等價(cast運算)指派(右邊結果給左邊)
先宣告 特定型態變數 再建立其敘述
char c; //先宣告 字元型態的變數
c = (char)System.in.read();//再建立其敘述
=====================================================
你會問 可是我要輸入 數字ㄟ!!!
在程式中 數字的輸入 較占多數 因為要計算一堆東西
確實~~~
那要如何輸入數字呢???
在探討如何輸入 數字 之前
我們先來討論
數字(數值) 到底 算是 一個字元呢???? 還是 一個字串(字元陣列)???
0是一個數字 也是一個字元
1 是一個數字 也是一個字元
2 是一個數字 也是一個字元
3 是一個數字 也是一個字元
4 是一個數字 也是一個字元
5 是一個數字 也是一個字元
6 是一個數字 也是一個字元
7 是一個數字 也是一個字元
8 是一個數字 也是一個字元
9 是一個數字 也是一個字元
注意!!!!!
10 是一個數字 但並非一個字元 是一字串!!!
想法一、請問在數值世界中
我們可能只需要處理0~9這幾個數字嗎??
No!!
這裡電腦直接斷定了他只能把數字視為字串
這樣才能和它做溝通
你想也是班上五十個人都支持A同學當班長
就十個支持B同學當到頭來還是由A來擔任
這是少數服從多數的概念
想法二.
我們從資料型別記憶體佔的大小來做
判定吧!!!
Integer(整數)
====================
byte (位元組) --> 8 bits
short(短整數) --> 16bits
int(整數) --> 32bits
long(長整數) --> 64bits
====================
Float、Double(浮點數)
====================
float(單精確浮點) --> 32 bits
double(雙精確浮點) --> 64 bits
====================
char(字元)
====================
char(字元) --> 16bits
====================
想法三. 當然我們也可以看看程式碼後頭給的資訊
做判定 後面的參數基本上都是以String來代表
雖然藉由鍵盤所輸入的數字會被視作字串,但只要經過
資料轉換即可把字串變數值搂~~
你說屁啦 最好 我不相信 於是 我代了字元 就顯示了 這個error message
好啦 回過頭來 我們得到一個結論
若要輸入數值 我們應該要先 了解 數值 屬於 字串
而只要我們搞懂 字串輸入的方法
即可輸入數值 你說是不是呢?????(激問修辭)
=============================================================
【字串的輸入】
首先 步驟1 及 步驟2 都跟剛剛一樣
之後 先宣告 物件 再建立物件敘述
BufferedReader keyin;//先宣告
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );//再建立敘述
物件~~~
先宣告 在建立
物件~~~
先宣告 在建立
=============================================================
【數值的輸入】

===============================
【無限輸入】字串:人名和對應的身高
(1.)字串比對思維
程式碼部分
輸出部分
public static void main( String[] args)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader keyin;
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
while( true )
{
System.out.println("輸入人名:");
String str_Name = keyin.readLine();
String badName_for_break = "Bitch";
System.out.println("輸出人名:" + str_Name );
if( str_Name.equals(badName_for_break))
{
System.out.println("This is not a good name OK");
break;
}
System.out.println("輸入身高:");
//method1. 一行搞定
String str = keyin.readLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("輸出其身高數值(字): "+ num);
}
}
(2.)限制次數思維
程式碼部分

輸出部分

public static void main( String[] args)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader keyin;
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println("輸入人名:");
String str_Name = keyin.readLine();
String badName_for_break = "Bitch";
System.out.println("輸出人名:" + str_Name );
System.out.println("輸入身高:");
//method1. 一行搞定
String str = keyin.readLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("輸出其身高數值(字): "+ num);
}
System.out.println("只能給你輸入三次以跳出loop");
}
=================================
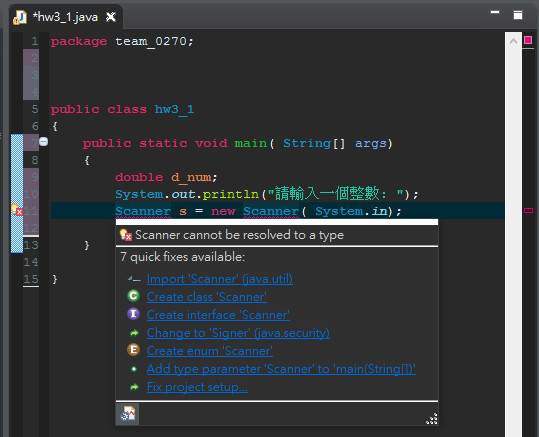
【如何利用Scanner類別進行輸入】
進入我們主軸
【基本設定】
Scanner 數值的輸入
import java.util.Scanner
偷看一下後面給的提示
用 .nextDouble() 去 輸入
only reads the next 4 bytes from the input stream
當你是用 int 做宣告時
這是不能用 .nextDouble() 或是.nextLong()
記憶體空間不足無法轉換
還有可能是強制轉換的限制
(大範圍 轉 小範圍 數值資料 需用到cast運算)
換成 .nextInt() 或是 .nextShort()
是可以被接受的
public static void main( String[] args)
{
int d_num;
System.out.println("請輸入一個整數: ");
Scanner s = new Scanner( System.in);
d_num = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("輸出數值:" + d_num);
}
==============================Scanner 字串的輸入
.nextLine()
//會印出整行,不會因為空白而斷句
.next()//不會印出整行 ,會因為空白而斷句
這是本次基礎學習歷程經驗分享
大家以前是否還習慣著 C 或 C++
以前如果們要實行無限輸入一個整數這種功能的話
我們會怎麼做???
感覺 while 迴圈不可少
首先我們先不要急著 無限輸入
先輸入一個數字 即可
輸入是致命關鍵 不可不會!!!!!
【字元的輸入】
Step1. 請載入 java.io.* 套件 ( 口訣: 爪哇點矮喔點心 / 怕你少輸入 任何一個符號)
Step2. 在 main方法後頭 加上 throws IOException 要加喔!!!!!!
Step3.宣告字元 我們要輸入一個字元型態的鍵盤key-in的任意字符
並等價(cast運算)指派(右邊結果給左邊)
先宣告 特定型態變數 再建立其敘述
char c; //先宣告 字元型態的變數
c = (char)System.in.read();//再建立其敘述
=====================================================
你會問 可是我要輸入 數字ㄟ!!!
在程式中 數字的輸入 較占多數 因為要計算一堆東西
確實~~~
那要如何輸入數字呢???
在探討如何輸入 數字 之前
我們先來討論
數字(數值) 到底 算是 一個字元呢???? 還是 一個字串(字元陣列)???
0是一個數字 也是一個字元
1 是一個數字 也是一個字元
2 是一個數字 也是一個字元
3 是一個數字 也是一個字元
4 是一個數字 也是一個字元
5 是一個數字 也是一個字元
6 是一個數字 也是一個字元
7 是一個數字 也是一個字元
8 是一個數字 也是一個字元
9 是一個數字 也是一個字元
注意!!!!!
10 是一個數字 但並非一個字元 是一字串!!!
想法一、請問在數值世界中
我們可能只需要處理0~9這幾個數字嗎??
No!!
這裡電腦直接斷定了他只能把數字視為字串
這樣才能和它做溝通
你想也是班上五十個人都支持A同學當班長
就十個支持B同學當到頭來還是由A來擔任
這是少數服從多數的概念
想法二.
我們從資料型別記憶體佔的大小來做
判定吧!!!
Integer(整數)
====================
byte (位元組) --> 8 bits
short(短整數) --> 16bits
int(整數) --> 32bits
long(長整數) --> 64bits
====================
Float、Double(浮點數)
====================
float(單精確浮點) --> 32 bits
double(雙精確浮點) --> 64 bits
====================
char(字元)
====================
char(字元) --> 16bits
====================
想法三. 當然我們也可以看看程式碼後頭給的資訊
做判定 後面的參數基本上都是以String來代表
雖然藉由鍵盤所輸入的數字會被視作字串,但只要經過
資料轉換即可把字串變數值搂~~
你說屁啦 最好 我不相信 於是 我代了字元 就顯示了 這個error message
好啦 回過頭來 我們得到一個結論
若要輸入數值 我們應該要先 了解 數值 屬於 字串
而只要我們搞懂 字串輸入的方法
即可輸入數值 你說是不是呢?????(激問修辭)
=============================================================
【字串的輸入】
首先 步驟1 及 步驟2 都跟剛剛一樣
之後 先宣告 物件 再建立物件敘述
BufferedReader keyin;//先宣告
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );//再建立敘述
物件~~~
先宣告 在建立
物件~~~
先宣告 在建立
=============================================================

===============================
【無限輸入】字串:人名和對應的身高
(1.)字串比對思維
程式碼部分
輸出部分
public static void main( String[] args)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader keyin;
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
while( true )
{
System.out.println("輸入人名:");
String str_Name = keyin.readLine();
String badName_for_break = "Bitch";
System.out.println("輸出人名:" + str_Name );
if( str_Name.equals(badName_for_break))
{
System.out.println("This is not a good name OK");
break;
}
System.out.println("輸入身高:");
//method1. 一行搞定
String str = keyin.readLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("輸出其身高數值(字): "+ num);
}
}
(2.)限制次數思維
程式碼部分

輸出部分

public static void main( String[] args)throws IOException
{
BufferedReader keyin;
keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println("輸入人名:");
String str_Name = keyin.readLine();
String badName_for_break = "Bitch";
System.out.println("輸出人名:" + str_Name );
System.out.println("輸入身高:");
//method1. 一行搞定
String str = keyin.readLine();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("輸出其身高數值(字): "+ num);
}
System.out.println("只能給你輸入三次以跳出loop");
}
=================================
【如何利用Scanner類別進行輸入】
進入我們主軸
【基本設定】
Scanner 數值的輸入
import java.util.Scanner
偷看一下後面給的提示
用 .nextDouble() 去 輸入
only reads the next 4 bytes from the input stream
當你是用 int 做宣告時
這是不能用 .nextDouble() 或是.nextLong()
記憶體空間不足無法轉換
還有可能是強制轉換的限制
(大範圍 轉 小範圍 數值資料 需用到cast運算)
換成 .nextInt() 或是 .nextShort()
是可以被接受的
public static void main( String[] args)
{
int d_num;
System.out.println("請輸入一個整數: ");
Scanner s = new Scanner( System.in);
d_num = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("輸出數值:" + d_num);
}
==============================Scanner 字串的輸入
.nextLine()
//會印出整行,不會因為空白而斷句
.next()//不會印出整行 ,會因為空白而斷句
這是本次基礎學習歷程經驗分享





















留言
張貼留言